Numerical control machining process and division of work steps
Machining parts on CNC machine tools, the process can be more concentrated, and most or all of the processes are completed as much as possible in one setup. There are several ways to divide the general process:
1) Division process according to part mounting position
Due to the different structural shapes of each part, the technical requirements of each machined surface are also different, so the positioning methods are different when processing. Generally, when the shape is processed, it is positioned in an inner shape; when the inner shape is processed, it is positioned in an outer shape. Therefore, the process can be divided according to the positioning method.
The sheet cam shown in Figure 2-17 can be divided into two processes according to the positioning method. The first process can be performed on a common machine tool. The inner holes of the end faces A and Φ22H7 are machined on the outer circular surface and the B plane, and then the process holes of the end faces B and Φ4H7 are processed; the second process is to position the processed two holes and one end face, and the cam is milled on the numerical control milling machine. Outer surface curve.
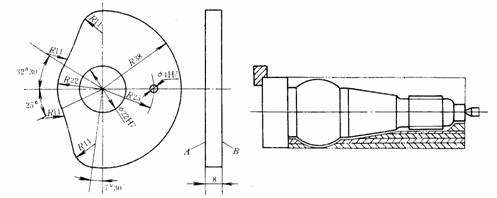
Figure 2-17 Chip cam Figure 2-18 Turned parts
2) Roughing and finishing division process
When the process is divided according to factors such as machining accuracy, rigidity and deformation of the part, the process can be divided according to the principle of coarse and fine machining, that is, roughing and finishing. This can be done with different machine tools or different tools. Usually in one installation, it is not allowed to machine a part of the surface of the part before processing the other parts of the part. As shown in Figure 2-18, the majority of the entire part of the part should be removed first, and then the surface of the part is refined to ensure the processing accuracy and surface roughness requirements.
3) According to the tool division process
In order to reduce the number of tool changes, compress the dead time, and reduce unnecessary positioning errors, the parts can be machined according to the method of tool concentration, that is, in one setup, all the parts that may be processed are processed by the same tool as much as possible, and then Then change another knife to process other parts. This method is often used in dedicated CNC machine tools and machining centers.
(2) Division of work steps
The division of work steps is mainly considered from the aspects of machining accuracy and efficiency. It is often necessary to use different tools and cutting amounts in one process to machine different surfaces. In order to facilitate the analysis and description of more complex processes, it is subdivided into steps in the process. The following takes the machining center as an example to illustrate the principle of division of work steps:
1) The same surface is finished in the order of roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing, or the entire surface is separately processed by roughing and finishing.
2) For parts with both milling and boring, the surface can be first boring and then restored for a period of time, which can reduce the influence of the deformation on the accuracy of the hole.
3) Divide the work steps by tool. Some machine tables have shorter turnaround times than tool change times. Worksteps can be divided by tool to reduce the number of tool changes and increase machining productivity.
In short, the division of processes and work steps should be considered comprehensively based on the structural characteristics and technical requirements of specific parts.
The flush plate is an essential component of a concealed installation system that remains visible to the user. Fabia, a brand that pays great attention to design elements and reliable functionality, offers a range of flush plates with different designs, materials, colors, and finishes. These flush plates not only serve as switches for flushing but also provide access to the hidden water tank for maintenance purposes.
Fabia manufactures flush plates primarily using three materials: ABS plastic, stainless steel, and glass. Each material offers unique aesthetic and functional characteristics to complement the overall bathroom design. The choice of material depends on the customer's preference and the desired visual appeal.
In terms of functionality, flush plates can be categorized into three types: mechanical (manual pressing), pneumatic, and sensor-based. Mechanical flush plates require manual pressing to initiate the flushing process, providing a traditional and tactile experience. Pneumatic flush plates utilize air pressure to trigger the flushing mechanism, offering a touchless operation. Sensor flush plates use advanced technology to detect the user's presence and automatically activate the flushing system, providing a convenient and hygienic solution.
The majority of flush plates available on the market are dual flush panels, which allow users to choose between two flush volumes based on water consumption. Typically, a short flush consumes around 3 liters of water, while a long flush utilizes 4.5 to 6 liters. The dual flush button design is the most common type of flush plate, ensuring both economic and environmental savings by promoting water conservation.
In a word, Fabia's flush plates are designed to combine functional efficiency with aesthetic appeal. By offering a variety of materials, designs, and functional options, Fabia enables customers to select the flush plate that best suits their needs and preferences while promoting water-saving practices and enhancing the overall bathroom experience.
Flush Plate, Toilet Push Button, Toilet Button Panel, Flush Button, Toilet Flush Panel
Guangdong Fabia Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.smartfabiatoilet.com
