How to choose the best thread fastener?
Manufacturers often need to purchase a variety of general-purpose parts, and the general parts are mainly fasteners. Fasteners are mostly screw-fastened, which are the screws and bolts we use.
In the process of purchasing screws, people often only pay attention to diameter, length and material. But in fact, there are a lot of important information about the thread, and there is also a lot of learning.
Today we briefly introduce the small knowledge of the shape of threaded fasteners.
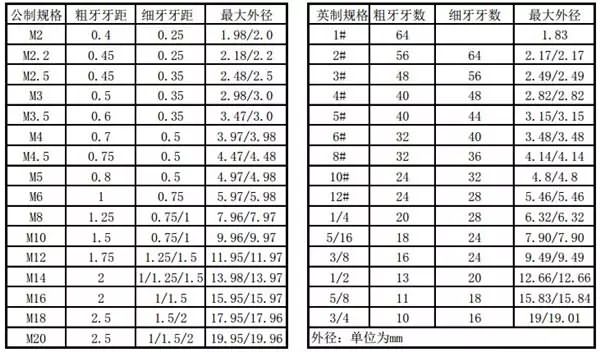
Nominal diameter, pitch, lead, screw length, screwing method
The nominal diameter is the basic information, and other information is checked against the nominal diameter.
The nominal diameter represents the specific size of the thread. In layman's terms, it is the size of the thread.
The nominal diameter is divided into 3 series:
The first series is the preferred thread in the design. It is very common and is generally available in stock.
The second series is the thread that is not commonly used in the design. Suppliers generally do not stock up in advance, and should communicate in a timely manner if needed.
The third series is the thread that is avoided as much as possible in the design. Very little use. If you purchase, please communicate with the supplier in advance.
The following are the specific nominal diameter values ​​(unit: mm) of the three series:
Series 1: 1, 1.2, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 90, 100, 110, 125, 140, 160, 180, 200, 220, 250, 280
Series 2: 1.1, 1.4, 2.2, 3.5, 4.5, 7, 14, 18, 22, 27, 33, 39, 45, 52, 60, 68, 76, 85, 95, 105, 115, 120, 130, 150, 170, 190, 210, 240, 260, 300
Series 3: 5.5, 9, 11, 15, 17, 25, 26, 28, 32, 35, 38, 40, 50, 55, 58, 62, 65, 70, 75, 78, 82, 135, 145, 155, 165, 175, 185, 195, 205, 215, 225, 230, 235, 245, 255, 265, 270, 275, 285, 290, 295
The above data does not list the first and second series of small threads. Small threads have a nominal diameter ranging from 0.3mm to 1.4mm.
There is also a nominal diameter of 35mm, which is only used for the lock nut of the bearing.
The two pitches and leads are required to be bundled.
There are two types of pitch: coarse and fine. Coarse teeth are commonly used models for large tensile and impact forces. Fine thread is used in places where pre-tightening force is required. Because the fine thread has higher self-locking property than coarse thread, the pre-tightening force is also larger; where precision is required, such as the thread on the seal; where the design is limited, If the structure is required to be compact.
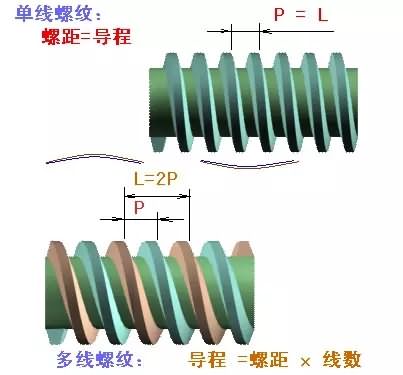
The lead refers to the axial distance moved by any point on the thread along the same spiral. Please pay attention to the same spiral! So this introduces a new concept: the number of threads. The threads are divided into single thread and multi thread. When the pitch is equal to the lead, it is a single thread. Single thread is the most common type. When the pitch is half or less than the lead, it is a multi-thread. Multi-thread threads are typically used in the transmission of fast mechanisms.
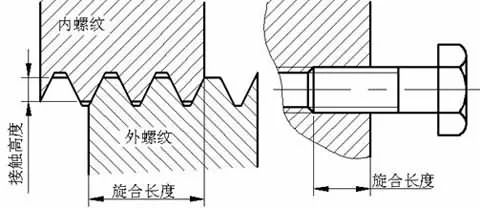
The length of the screw generally refers to the length of the thread on the fastener, the seal, and the transmission member. The screw length is generally not greater than the total length of the part. The length varies according to different requirements. "Full filament" means that the threaded area covers the entire screw area. "Half-wire" means that the threaded area is equal to the area occupied by the non-threaded area. In general, the longer the length of the stitching is, the lower the accuracy is because of the inevitable interference in the screwing process. At the same time, the short length of the screw will cause the connection to be unreliable. Therefore, you should choose a short twist length as much as possible while ensuring a reliable connection.
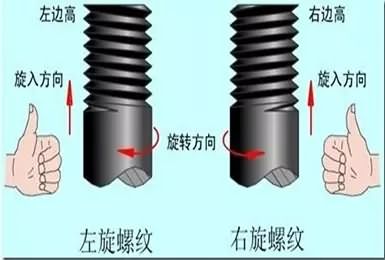
The screwing method is divided into left-handed and right-handed. Among them, right-handed disassembly is convenient, and the performance after processing is better than left-handed, so it is more common. The use of left-handed rotation is generally two cases. One is to distinguish. The second is to prevent looseness. For example, the part that rotates clockwise at a high speed must use the reverse tooth, because the tooth may loosen during the clockwise rotation of the machine, and the anti-tooth will become tighter.
The Torch body is the key component of the tig welding torches .They are the channel of the water or the gas pass through ,like a connector .Each series of the torch bodies have four types ,the common type , the flexible ,the valve ,the flexible and the valve . The function of each torch bodies is different ,the flexible improves torch control in limited-access area ,the customer can choice based on their need .


Valve Tig Torch Body, Pencil Tig Torch Body, WP-17 Tig Torch Body, WP-26 Torch Body
EDAWELD COMPANY LIMITED , https://www.jsedaweld.com
