Planting structure adjustment and changes in herbicide use technology
In recent years, due to the fluctuation of agricultural product prices, the economic benefits of farmers have declined, and the adjustment of crop production structure is inevitable. The national “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan†requires the use of “zero growth†for fertilizers and pesticides to ensure the task of increasing production and quality. Herbicides are the key and difficult. It is mainly caused by serious phytotoxicity and poor control of refractory weeds, as well as resistance problems, and poor economic returns. The use of good herbicides requires solving five problems, and it is necessary to be familiar with the perfect combination of herbicides and use techniques, agronomic measures, plant protection machinery and their standardized use techniques.
1 Control weeds to innovate theory and change concepts
1.1 Control weed damage instead of destroying
There are nearly a thousand species of weeds in the country, and there are 20 to 30 species that cause damage to crops. According to the study, there are more than 50,000 weed seeds per square meter in 30 cm of ploughing. Due to the biological characteristics of weeds, depth and dormancy, weed seeds are germinated and unearthed every year, and mature seeds are returned to the soil, always changing the total number. In a small state, no matter how much the people pay for weeding, weeds can't be eliminated. Some weeds can be associated with crops, such as planting wood rhinoceros between wheat, and planting small crown flowers in corn fields, which have the effects of increasing soil fertility, supplying crop nutrients, and promoting growth.
To change the concept, overcome the ignorance and human selfishness, we must learn to live in harmony with weeds. Do not kill or kill weeds, but use comprehensive measures such as agronomy, chemistry, machinery and other measures to control the hazards.
Since the herbicides have been used, some people believe that herbicides are omnipotent, neglecting the learning, selection and use of herbicides, selecting suitable plant protection machinery and standard use techniques, and the scientific application of agronomic measures, resulting in an increase in the number of refractory weeds. The phytotoxicity is serious.
1.2 Improved herbicide efficacy evaluation method
To change the herbicide efficacy evaluation method, the weed fresh weight reduction rate instead of the quantitative method, weed fresh weight reduction of more than 80% can effectively control weed damage, especially perennial weeds, inhibit growth, does not affect crop growth and yield And economic benefits.
The use of various agronomic, herbicide, and mechanical measures to control weed hazards within the allowable thresholds of economic, ecological, and social effects.
At present, most of the serious use of herbicides is to eliminate a certain weed, excessive use and repeated use of herbicides, reducing production by 40% to 60%, and even production. The northeastern part of Inner Mongolia and the northwestern part of Heilongjiang Province are used to control soybean fields. The dosage of sulfamethoxazole is increased by 4 to 8 times, and the phytotoxicity is serious. In August 2016, the drought was severe, and large areas were out of production, which was caused by drought.
Invasive weeds may cause harm in a short period of time. As time goes by, crops and weeds adapt to each other, which will inhibit the specific reproduction of these alien species, transform them into common weeds, and gradually reduce the harm.
2 How to choose herbicide
2.1 Selection of herbicides and herbicides based on efficacy and safety
The period of use of herbicides can be divided into pre-emergence and post-emergence application. Pre-emergence application can be divided into autumn and spring before sowing, and pre-emergence application after sowing; post-emergence application can be divided into early post-emergence, mid-emergence, and late post-emergence application.
Compared with pre-emergence and post-emergence herbicides, which kind of application period is better? First, according to the complex climate change in China, the characteristics of weeds occur, and the types are heterogeneous. The occurrence time is long in the north and relatively concentrated in the south. To compete for nutrition from weeds and crops, affect growth and yield considerations, the use of herbicides is better than late use, and it is best to control weeds in the early stages before they occur. The herbicide pre-emergence use increased the efficacy by 10%-20% after the seedling, and increased the yield by 10%-30%. Among them, the herbicide used in the northern autumn was the best for the safety and efficacy of the crop, and the yield increased by 5% compared with the spring pre-emergence application. ~8%, improve the efficacy of 5% to 10%.
Soybeans, corn, potatoes, rice, sugar beets, peanuts, pumpkins, vegetables, cotton, orchards should be pre-emergence herbicides, supplemented by post-emergence herbicides, and should account for more than 85% of pre-emergence (including autumn application). More than 20%, spring application accounted for 50% to 60%), post-emergence application accounted for less than 15%.
The rice transplanting field is mainly closed by soil, supplemented by post-emergence stem and leaf spray, and the northern transplanting field is promoted and applied in stages. 100 to 7 days before transplanting is 100%, and 15 to 20 days after transplanting according to grass conditions. The second application was carried out.
2.2 Choose a safe herbicide
Choose the safety of the herbicide variety first, try not to choose long residual herbicides, if there is no alternative variety, you can reduce the mixture of drugs.
Heilongjiang Land Reclamation Bureau Plant Protection Station since 1990, for soybeans (including cowpea, red bean, mung bean, etc.), corn, wheat (including barley, oats), rice, rape, beets, sorghum, millet, potato, melon (watermelon, Pumpkin, melon, sunflower, peanut, alfalfa and other crop herbicides were systematically evaluated for safety and residual hazards. For herbicide varieties, field efficacy trials were generally performed for 3 to 5 years, and more were done 6-8. In the year's experiment, the study concluded that a variety of herbicides registered in a crop have obvious differences in the safety of crops, and cannot be selectively selected according to the price. Therefore, we divide herbicides into three categories, one for recommended use; the second for restricted use; and the third for eliminated (not recommended).
Compared with safer herbicides, the poor yield of rice is 100-200 kg per mu, and the yield is reduced by 20% to 40%; the yield of soybean is 50 kg or more per acre, and the yield is reduced by 25% to 30%; mixed formula and mixed The yield between the preparations is 30-100 kg per acre. The use of 2,4-butyl butyl ester in wheat fields can reduce wheat yield by 7% to 26%.
Crop planting structure adjustment should pay special attention to long-lasting herbicides. These herbicides have a long residual time in the soil, generally up to 2 to 3 years, and can be as long as 4 to 5 years. Although there is no herbicidal action, they can cause phytotoxicity to the sensitive crops of the lower jaw, and the lighter can inhibit the growth of the crop. Production is reduced, and severe crops cause death and production.
The main long-term residual herbicides are atrazine, metsulfuron, chlorsulfuron (chlorsulfuron), imazamox, imidazolidinic acid, flufenazone, chlorsulfuron, oxazinone, clomazone , oxasulfuron, nicosulfuron, simazine, ethametsulfuron, chlorsulfuron, flusulfuron, flufensulfuron, flufenacet, flusulfuron, chlorsulfuron Long, ether benzosulfuron, imazaquin, mesoxalam, clopyral acid and the like.
Herbicides should also pay attention to drifting phytotoxicity. Drifting can reduce the herbicidal effect of crops, pollute the environment, and harm sensitive crops. Herbicides that are easy to drift and volatilize, such as 2,4-butyl butyl ester, chlorpyrifos, trifluralin, sec-butyl, and clomazone. 2,4-butyl butyl ester, dysentidone, etc., when the temperature is above 15 °C, it begins to volatilize and drift, and increases with the increase of temperature. Under the condition of inversion temperature, it can drift over a long distance, reaching several kilometers, jeopardizing a variety of sensitive crops. .
2.3 Adjusting the structure of herbicides for refractory weeds
For many years, the use of herbicides in the field of weeds has decreased, and the number of refractory weeds has increased. Effective herbicides should be selected for refractory weeds in the field.
(1) Types of refractory weeds
The types of refractory weeds in China include wild carp, stalk, stalk, stalk, rice, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk, stalk Roots, stalks, big nests, coiled stalks, Solanum nigrum, Xanthium, Eriocheir sinensis, Stellera, Purslane, Po Po, Pork, Cattle, Boar, Artemisia Morning glory, thorny vegetables, big thorns, wenjing, sorrel, sauerkraut, reed, shui, wild sage, diarrhea, rain long flower, sage, hollow lotus seed, fragrant aconite, flat stalk Valerian, Sanjiang sedge, valerian, etc.
(2) Selecting herbicides according to the type of refractory weeds, rational mixing
For example, rice transplanting fields control flat stalks of alfalfa, alfalfa, and Sanjiang alfalfa. Before transplanting, pyrazosulfuron-methyl or pyrithione-propionamide effervescent tablets are selected. After transplanting, bentazone and pyrazosulfuron-methyl are selected. , pyrimidine ether, bispyribyl ether, or oxazolone, or oxazinone + pyrazosulfuron.
Another example is cornfield control of leeks, thorns, comfrey, pre-emergence of flufensulfuron, thifensulfuron, or sulffenapyr + thiophenesulfuron + atrazine, or pyrisulfuron Amine + 2, 4 drops of isooctyl ester + atrazine mixed. After the seedling, nicosulfuron + bentazone, or sulfamesulfuron + thifensulfuron (north), or bentazone + atrazine.
3 Pay attention to the prevention of phytotoxicity
3.1 The agronomic measures to prevent phytotoxicity are the most important
3.1.1 To be planted at an appropriate time
The problem in agricultural production is that the selection of crop varieties does not leave the slam, and it is wrong to think that early planting will grab the accumulated temperature. Seeding is too early, the temperature is low, the immune function of the crop seedlings is reduced, the emergence of seedlings is late, the growth and development is slow, the phytotoxicity is heavy, the disease is susceptible, the disease is heavy, and the gluttony is ripe for late reduction.
The traditional sowing period is to calculate the growth period and sowing date based on the average temperature and stable temperature through 10 °C without applying fertilizer or pesticide. After years of research and practice, the daily average temperature is stable through 13 °C to calculate the new standard of growth period and sowing date, which is the high-yield period. The new method of selecting crop varieties is to retreat to a accumulated temperate zone. Stable production, high yield and high quality.
3.1.2 Control the depth of sowing
The whole land should be flat and the seeding depth must be consistent. Seeding too deep seedlings consumes nutrients, causing weak seedlings and phytotoxicity.
3.2 Administrative measures can effectively prevent phytotoxicity
3.2.1 Do a good job of safe use of zoning
Develop safe use of pesticide programs and economic crop zoning to limit the use of certain drifting herbicides in cash crop planting areas.
3.2.2 Improved herbicide dosage form
A herbicide such as 2,4-butyl butyl ester which is liable to cause drifting damage is replaced with 2,4-diisooctyl ester. Improve the dosage form of the dysentery, which can effectively solve the problem of volatile migration and phytotoxicity.
4 Adhere to the traditional effective agronomic measures
4.1 Reasonable rotation, close planting, etc.
Simultaneous evolution of crops and weeds, all kinds of crops have associated weeds and crop ecotypes. By changing crops, changing herbicides can effectively control the weeds of crops and avoid weeds. Close planting helps to inhibit certain refractory weeds.
4.2 Rational farming
The main problem of current agricultural farming is shallow ploughing, shallow ploughing, only 10-15 cm, soil compaction, hard, roots can not continue, the soil is impervious to water, airtight, neither drought-resistant nor anti-mite, aggravating phytotoxicity. It is imperative to break the bottom of the plow, adopt mechanical deep-deep, deep and shallow alternate farming measures, and turn over once every 2 to 3 years to improve the physical and chemical properties of the soil, and chop the roots of the perennial grassland. After drying, 70% can be eliminated. The use of herbicides in the lower jaws is effective.
4.3 Give full play to the mechanical role to effectively control weed damage
4.3.1 Early spring flooding, staged sowing control weeds
According to the different characteristics of weed emergence period, weaving weeds induced by mechanical early spring planting, weeding by staged sowing and staging, and increasing the ground temperature by preserving, promoting the early emergence of crop seeds, which is conducive to the cultivation of strong seedlings.
4.3.2 Cultivating soil control measures
Since the use of herbicides, some wrong practices, such as the use of herbicides, should not be grounded, fearing that cultivating destroys the film and affects the weeding effect; or that it can be ploughed less and saves costs. The result is a batch of weeds after a rain, and then have to Use the herbicide once.
Regardless of whether pre-emergence or post-emergence herbicides are used for timely cultivating, cultivating is beneficial to weed control, and early cultivating is beneficial to increase ground temperature and promote seedling growth. Later deep cultivating is beneficial to control diseases, drought resistance, flood control and lodging prevention. Generally cultivating 3 to 4 times. During the arching period of the crop, the shallow loose soil was ploughed, and 2 to 3 times of cultivating was carried out after the seedling. The last time was to cultivate the soil and seal the ridge.
4.3.3 Agronomic measures should be adapted to mechanical operation measures
At present, there is a misunderstanding in agricultural production. Some people think that machinery should adapt to agronomic measures. For example, corn and soybean in the cold regions of northern China are densely ridged. In the case of poor mechanization standards and low level of agronomic and herbicide use technology, it has appeared in recent years. The chemical weeding failed, the large ridge cultivation can not carry out the cultivating, which leads to the reduction of grassland. It is best to change back to the small ridge cultivation if there is no condition.
5 Plant protection machinery standardization and promotion of its standard use technology
Plant protection machinery is the basic tool for spraying herbicides. The standardization and standardization of plant protection machinery is an agronomic measure. It is recommended that the state increase the training of plant protection machinery and the popularization of its technical specifications. It is an important task for reducing the amount of herbicides, reducing phytotoxicity, increasing production and income. First of all, the agricultural technicians and plant protection machinery operators are taught, trained and trained in plant protection machinery standards and technical specifications.
5.1 Plant protection mechanical spray effect evaluation standard
(1) The effective diameter of the sprayed droplets is used as the evaluation standard
Spraying the post-emergence herbicide is suitable for spraying droplets with a diameter of 250-400 μm. After spraying the seedlings, the herbicide is suitable for spraying droplets with a diameter of 300-400 μm.
(2) Using the spray droplet density of the herbicide spray as the evaluation standard
The spraying pre-emergence herbicide has a suitable droplet density of 30-40 pieces/cm2, and the suitable droplet density of the herbicide after spraying is 30-40 pieces/cm2, and the contact density is 50-70 pieces/cm2.
(3) spraying mist droplets on plant leaf surface residence time
The herbicide sprayed on the weed leaves requires a certain residence time. Generally, the water-soluble herbicide can be washed away from the weed leaves by a rain of 1 to 2 mm; the oil-soluble herbicide can be removed from the weeds by a rainfall of 5 to 10 mm. The leaves are washed away.
5.2 Matching of key components of the sprayer sprayer
(1) Choice of nozzle and filter
Spraying the herbicide with the sprayer and the knapsack sprayer should eliminate the cone nozzle and select the fan nozzle.
Spraying pre-emergence herbicides to select fan-shaped nozzles, equipped with 50 mesh column-type anti-drip filters; spraying post-emergence herbicides to select 80015 fan-shaped nozzles, with 100 mesh column-type anti-drip filters (high-powered spray bar sprayers use 8002) Fan-shaped nozzle with 50 mesh column anti-drip filter).
(2) Promote the external water quick-release nozzle body
Promote the external water quick-opening nozzle body, do not corrode the spray bar; replace the threaded nozzle body with the quick-installing nozzle body, easy to disassemble, not easy to damage the nozzle body, long service life, and eliminate the inner water-jet nozzle body.
(3) Preparing the navigator
The GPS navigator can make the herbicide spraying line straight, ensure uniform spraying of the liquid, and improve the herbicide utilization rate and work efficiency.
(4) Promote the spray mist uniformity test disk
It is easy to test the spray uniformity of the sprayer and the height of the boom.
(5) Promotion of pocket electronic weather instruments
It can accurately test the temperature, air relative humidity and wind speed during spraying operations.
5.3 Requirements for Spraying Herbicides on Sprayer Sprayers
(1) Spraying pre-emergence herbicides
The nozzle spacing is 50 cm, the spray pressure is 2 to 3 kg/cm2, the spray volume is 180-200 L/hm2, the spray bar is 50 cm from the ground, and the speed is 6-8 km/h. The high-power self-propelled sprayer sprayer has a spray pressure of 3 kg/cm2, a spray volume of 180-200 L/hm2, a boom height of 50 cm from the ground, and a vehicle speed of 12-18 km/h.
(2) Spraying post-emergence herbicide
Generally, the nozzle spacing is 50 cm, the spray pressure is 3~4 kg/cm2, the spray volume is 75-100 L/hm2, the spray bar is from the crop, or the weed top height is 46 cm, and the running speed is 6-8 km/h. The high-power self-propelled sprayer sprayer has a spray pressure of 4 to 5 kg/cm2, a spray volume of 75 to 100 L/hm2, a spray bar distance from the crop, or a weed height of 46 cm, and a running speed of 10 to 12 km/h.
5.4 Technical specifications for adjustment and use of sprayer sprayer
(1) Installation and adjustment of the sprayer sprayer;
(2) Field spray operations;
(3) cleaning of the sprayer;
(4) Security protection.
6 Promote the “two downs and one plus†spraying new technology
6.1 Reduce the amount of liquid spray
Spraying sprayer sprays pre-emergence herbicide spray volume of 180-200 L/hm2, sprayed herbicide spray volume of 75-100 L/hm2. The spray amount of the herbicide before artificial spraying is 225-300 L/hm2, and the spray amount of the herbicide after spraying is 100-150 L/hm2. The spraying amount of the herbicide before spraying on the aircraft is 30-50 L/hm2, and the spraying amount of the herbicide after spraying is 20-30 L/hm2.
6.2 Add vegetable oil spray aid
Spraying post-emergence herbicides under suitable meteorological conditions (temperature 13 ~ 27 ° C, air relative humidity greater than 65%, wind speed less than 4 m / s; generally before 8 o'clock in the sunny day, after 18 o'clock, it is best to spray at night without dew The best effect), the vegetable oil type spray auxiliaries use 0.5% of the spray volume, and the herbicide dosage can be reduced by 30% to 50%.
Spraying post-emergence herbicides under unsuitable meteorological conditions (high temperature and drought, temperature greater than 27 ° C, air relative humidity less than 65%, wind less than 4 m / s) and 1% of the amount of effluent weed control, weeding The dosage can be reduced by 20% to 30%.
6.3 Reduce the amount of medication
Under suitable meteorological conditions, the herbicide dosage can be reduced by 30% to 50%. Under the unsuitable meteorological conditions, the herbicide dosage can be reduced by 20% to 30%. The determination of the amount of herbicide used is based on the amount registered by the Ministry of Agriculture.
6.4 Post-emergence herbicide application period
The post-emergence herbicide application period is 2~4 leaf stage of annual broadleaf weeds, 3~5 leaf stage of grass weeds, perennial weeds are mostly 15-20 cm, and yarrow must be applied in 3 leaves, perennial Broad-leaved weeds are best applied before the 8-leaf stage, perennial weeds such as reeds 40 cm before application; perennial sedge weeds before the plant height of 15 cm.
More pesticide knowledge , please pay attention to China Pesticide Network
A double-convex lens is compose of two convex surfaces, has a positive focal length. Normally Bi-Convex lenses are most suitable where the object and image are on opposite sides of the lens, and are popular for many imaging applications.
Some styles of cylindrical lenses have antireflective coatings to increase the transmission of light through the lens. Fused silica cylinder lenses are ideal for demanding laser machining and medical applications.
We supply kinds of plano-convex Cylindrical Lens,plano-concave cylindrical lens,bi-convex cylindrical lens,bi-concave cylindrical lens,meniscus cylindrical lens,Rod cylindrical lenses,special cylindrical lens etc.Every sizes,materials cylindrical lenses are available according to your detailed parameters.
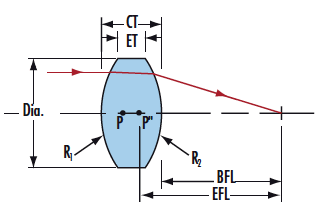
Double Convex Lens
Specification of our cylinderical lens as follow:
*Material: BK7,Ge,UV-grade fuse silica(JGS1,JGS2,JGS3)or other optical materials
*Dimension Tolerance: +0.0 -- -0.1mm
*Center Thickness: +/-0.1mm
*Focal Length Tolerance: +/-1%
*Surface Quality:20/10
*Surface Figure: lambda/2 at 633nm on plano side
*Clear Aperture>90%
*Chamfer: 0.25mm at 45 degree typical
*Coating Optional
Double Convex Lens,Double-Concave Cylinder Lens,Bi Concave Cylindrical Lens,Optical Glass Double-Convex Cylinder Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
